Level-2 News
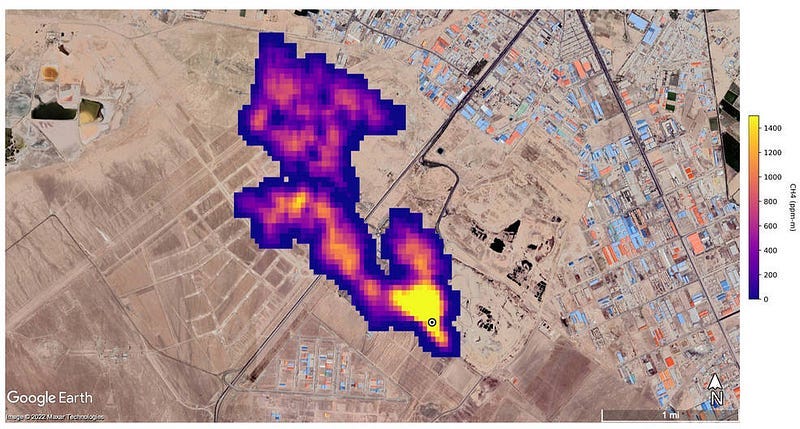
Methane ‘Super-Emitters’ Mapped by NASA’s New Earth Space Mission [link]
Originally, NASA’s Earth Surface Mineral Dust Source Investigation (EMIT) mission was designed to measure the mineral composition of Earth’s dust source regions to help scientists understand how they heat or cool our planet as dust travels across oceans. But while scientist were checking the accuracy of the image spectrometer’s mineral data they verified that EMIT could also detect the spectral fingerprints of methane. In fact, it can identify methane point sources quite exceptionally!
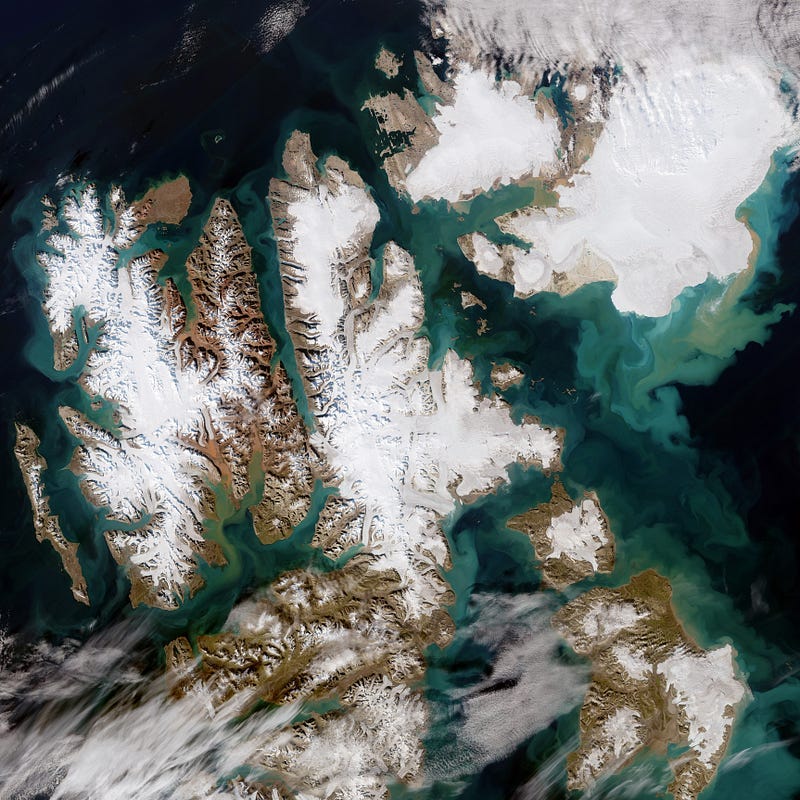

Svalbard — one of the fastest warming places on the planet [link]
“The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission captured this rare, cloud-free acquisition of the Norwegian archipelago. The image, captured on 21 August, shows the colourful and large sediment discharges in the Arctic Ocean.”
Tracking Ukraine cultural damage using satellite images [link]
A small team of UNOSAT experts, the United Nations Satellite Centre, study the difference in before-and-after satellite images. As of 24 October, the project has identified 207 damages sites.

ESA astronauts help map Europe’s light pollution from space [link]
“Astronauts have taken over a million pictures of Earth at night with digital cameras to demonstrate the true extent of light pollution. Recently, ateam of European researchers processed the pictures and compared them over time, showing a clear increase of lighting pollution in urban areas, and a shift towards whiter and bluer emissions, due to the widespread introduction of light-emitting diode lamps, or LED technology.
As Europe turns lights down in an urge to save energy, scientists warn that it should not only be about reducing bills — brighter nights are disrupting the night cycle for humans, animals and plants.”
ESA WorldCover 2021 map released [link]
The ESA WorldCover Team announced the release of the WorldCover 2021 map: 11 classes, 10m resolution, 77% overall accuracy independently validated.
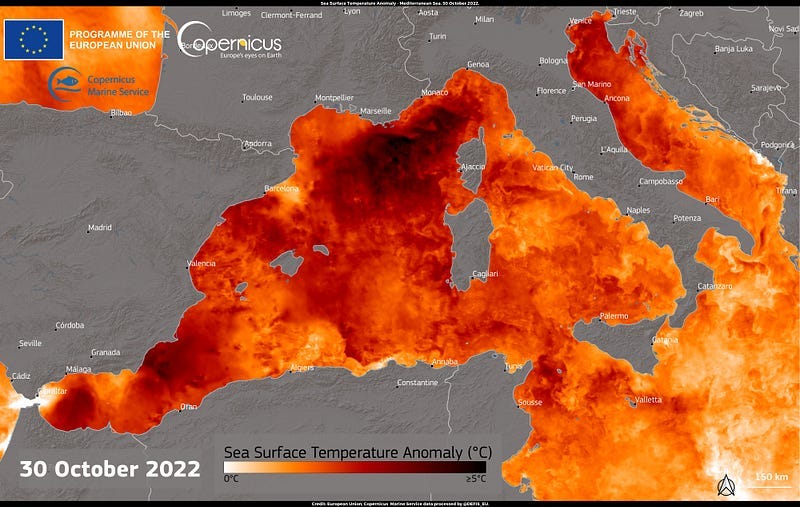
Sea Surface Temperature anomaly in the Mediterranean [link]
Data delivered by the Copernicus Marine Service (CMEMS) shows Sea Surface Temperature (SST) anomalies in the Mediterranean Sea, which is affected by the ongoing heatwave in Europe. The SST anomalies reached peaks of +5°C above average in some parts of the Mediterranean Sea off the Italian North-Western and the French South-Eastern coasts.
European Forest Fire report: Three of the worst fire seasons on record took place in the last six years [link]
Earlier this week, the Commission’s Joint Research Centre (JRC) published the latest edition of its Annual Report on Forest Fires in Europe, the Middle East and North Africa in 2021 [link]. It concludes that last year’s fire season was the second worst in the EU territory in terms of burnt area (since records began in 2006), after 2017 when over 10,000 km² had burnt. More than 5,500 km² of land burnt in 2021 — more than twice the size of Luxembourg — with over 1,000 km² burnt within protected Natura 2000 areas, the EU’s reservoir of biodiversity.
In 2015, EFFIS — European Forest Fire Information System — became one of the components of the Emergency Management Services in the EU Copernicus program.
Ozone Hole Continues Shrinking in 2022 [link]
Researchers at NASA and NOAA detect and measure the growth and breakup of the ozone hole with instruments aboard the Aura, Suomi NPP, and NOAA-20 satellites. The depleted area of the ozone layer over the South Pole was slightly smaller than last year and generally continued the overall shrinking trend of recent years.
ESA’s wind mission could help to forecast tropical storms [link]
In a recently published research, scientists found consistent differences between observations made by ESA’s Aeolus mission and estimates by the Hurricane Weather Research and Forecasting (HWRF) model — developed by NOAA.
NOAA’s JPSS-2 satellite to launch on Nov. 9th [link]
“JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) series and is designed to scan the Earth as it orbits from the North to the South Pole, crossing the equator 14 times a day to provide full global coverage twice a day. Operating from about 512 miles above Earth, JPSS-2 is expected to capture data to improve weather forecasts, helping scientists predict and prepare for extreme weather events and climate change.
JPSS currently includes two satellites — the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership, and NOAA-20. Upon reaching orbit, NOAA will rename the satellite NOAA-21.” The JPSS program includes five polar-orbiting satellites and is designed to provide sophisticated meteorological data and observations of atmosphere, ocean, and land for short-term, seasonal, and long-term monitoring and forecasting.
The legacy of TOPEX-Poseidon [link]
TOPEX-Poseidon, launched in 1992 as a joint US-French mission, revolutionised oceanography and transformed our understanding of climate by enabling oceanographers and climatologists to observe long-term variations in the ocean.
MTG-I1 payload is fit and well and ready for launch [link]
Read this blog post to learn more about a week of testing (and photos of experts “singing in the rain and searching for… coconuts”.
The Scene from Above Podcast - Season 13 is out! [link]
Season 13 is hosted by Ladies of Landsat and Sisters of SAR! Get to know them in Season 13 first episode!
Developer’s Orbit
Build a baseline model using Random Forests to classify fields by crop type from satellite images [link]
In this Jupyter Notebook by Radiant Earth Foundation’s MLHub you will use the “South Africa Crop Type Competition” training dataset to predict crop classes.
GeodataFlow: An opensource software library to design and run workflows on Geospatial & Earth Observation (EO) data [link]
GeodataFlow is a Python library for fetching, translating and manipulating Geospatial data (Raster, Vector, EO/STAC collections) by using a Pipeline or sequence of operations on input data.
Check these YouTube videos on how to get started with GeodataFlow [link]
Spatial Data Management with Google Earth Engine [link]
Learn how to retrieve, analyze, and manage spatial data using Google Earth Engine (GEE) and the geemap Python package.
Interesting read
How satellite data is helping tackle deforestation from global supply chains [link]
Rapid revisit deforestation detection with X-band SAR [link]
And staying on the topic of deforestation, read this to learn how folks at ICEYE developed a deep learning-based method to detect deforestation with SAR imagery.
Call for Volunteers
Get involved in Climatematch Academy! [link]
A group of computational climate scientists is putting together a climate foundations educational workshop next year and they are looking for interested volunteers to help put together the curriculum, which will be entirely based on Python and Jupyter notebooks and will rely heavily on Pangeo software.
Upcoming presentation
zen3geo: Guiding Earth Observation data on its path to enlightenment [link]
Join the Pangeo ML working group meeting at noon ET on Monday, November 07, 2022 for a presentation by Wei Ji Leong (Byrd Polar and Climate Research Center) on “zen3geo: Guiding Earth Observation data on its path to enlightenment”.
Take a look at the zen3geo walkthrough here.
Learning
OpenGeoHub Summer School 2022 videorecordings are out [link]
16 freely-accessible tutorials that cover R & Pyhton for earth systems and climate data. This year they also introduced JuliaGeo!
Must-watch: Accessing and using data cubes: spatial overlay, visualization and modeling — Python tutorial [link] + the accompanied Jupyter Notebook [link]
The workshop covers COG images, how to access and query a STAC catalog and training a Random Forest classifier.
ECMWF MOOC Machine Learning in Weather & Climate [link]
“Explore the application of Machine Learning across the main stages of numerical weather and climate predictions. These range from the acquisition and handling of input observations to their assimilation into models, and finally to forecasting and post-processing.”
Starting on 09/01/2023




